It’s frustrating to experience Wi-Fi issues on your Mac when you’re trying to stay productive or enjoy a seamless online experience. From slow connections to frequent dropouts, Wi-Fi problems can occur due to a variety of reasons.

Sometimes, it may happen after updating the latest macOS. Or, there may be some other causes such as network setting errors or software glitches.
Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to restore your Mac’s Wi-Fi to full functionality. In this article, we’ll look at how to fix macOS Sequoia Wi-Fi issues.
But first, let’s check a few things to make sure the issue is actually with macOS and not the Wi-Fi network itself.
- If you’re experiencing a problem with a specific app such as Slack or WhatsApp, check if the Wi-Fi is working on other apps.
- Check if the Wi-Fi network works on other devices connected to it, such as your iPhone or iPad.
If you’re experiencing Wi-Fi issues across multiple apps on your Mac and the network is working fine on other devices, proceed with the steps below to fix Wi-Fi issues on macOS Sequoia.
How to fix Wi-Fi issues on macOS Sequoia
1. Restart your router
One of the first things you should try to resolve Wi-Fi issues is to restart the router. To do so, turn off the router and disconnect it from its power supply. Wait for at least thirty seconds, and then plug it back in and power it on. Connect your Mac to the network and check if Wi-Fi works now.
Also make sure that:
- The router is not overheating. Ensure that it hasn’t been covered or placed at a location where there isn’t much ventilation.
- The router is not placed on or near any large metal surfaces. For instance, if it’s placed on a filing cabinet or near the radiator, it may not work correctly.

2. Turn off Wi-Fi and then turn it back on
This might seem simple, but it often works to fix any temporary glitches.
- On your Mac’s menu bar, click the Wi-Fi icon. If it’s not there, click Control Center and then the arrow next to Wi-Fi.
- Toggle off the Wi-Fi, wait for a few seconds and then toggle it on again.
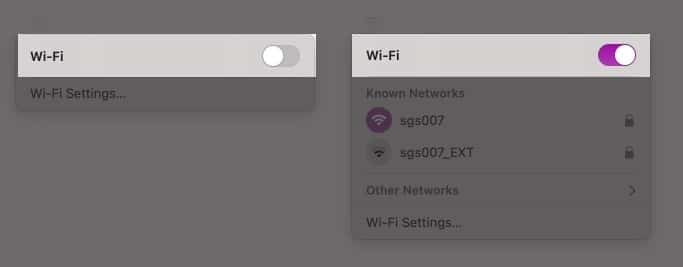
Check if this fixes the Wi-Fi issues you were facing,
3. Reboot your Mac
Restarting any device can often fix a lot of issues. This works for Wi-Fi issues on your Mac too.
- Click on the Apple menu and select Restart.
- In the dialog box, confirm by clicking the Restart button.
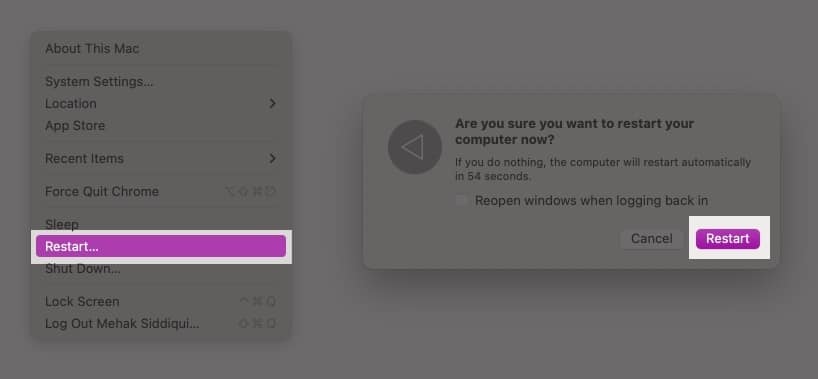
Once your Mac turns on again, check if the Wi-Fi is working.
4. Forget the Network and reconnect MacBook to it
Follow the steps below to reconfigure the W-Fi network on your Mac.
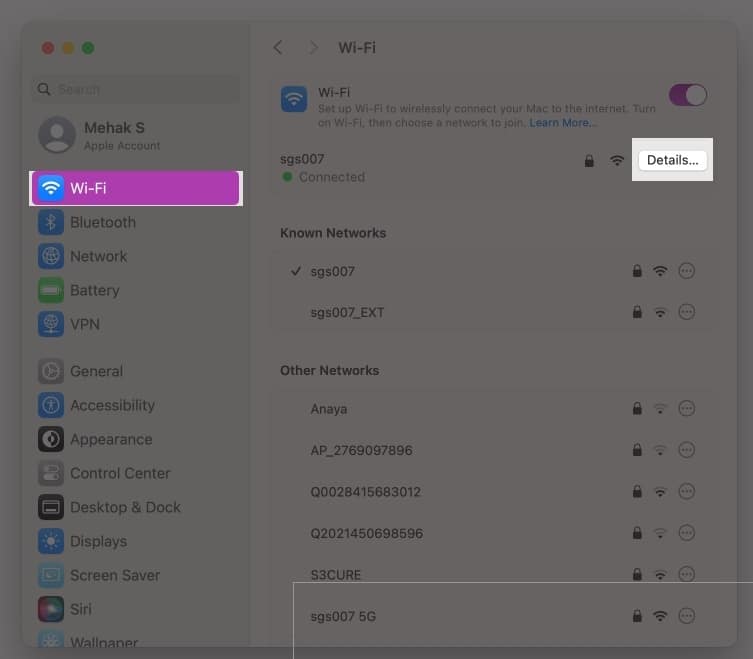
- Click on the Apple Menu and select System Settings.
- In the left pane, select Wi-Fi.
- Click Details next to the network you’re connected to.
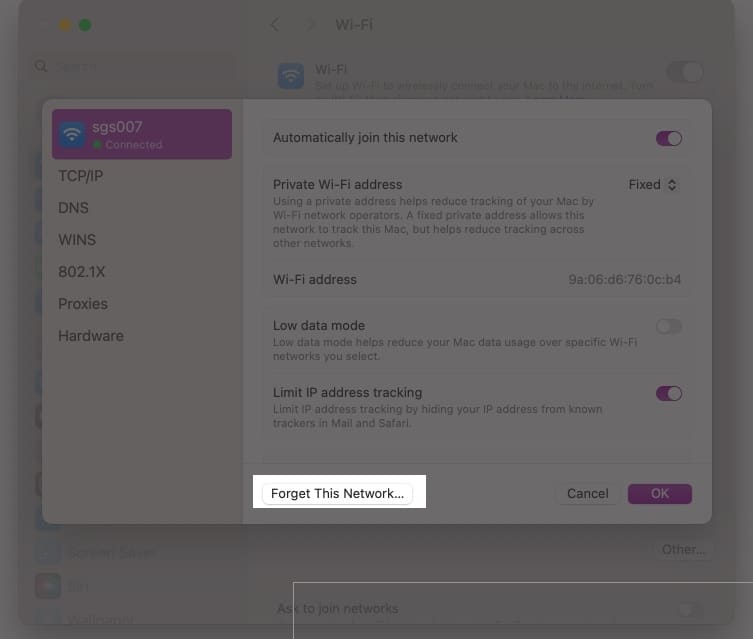
- Click on Forget This Network and then click Remove.
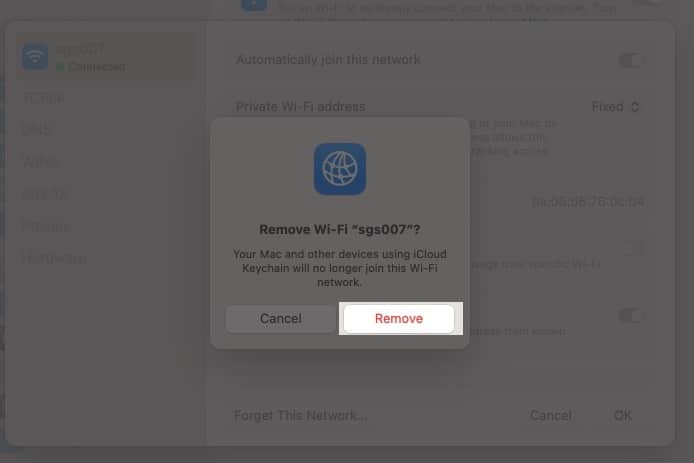
- Now, go back to System Settings → Wi-Fi and look for the name of your Wi-Fi network under Other Networks.
- Click Connect next to it and type in your Wi-Fi password.
Check if your Wi-Fi issues are resolved. If not, try the other methods below.
5. Change DNS Servers
DNS is what your Mac uses to translate domain names into IP addresses when you’re browsing the web. Changing DNS servers can help to fix Wi-Fi issues on macOS. Follow the steps below:
Become an iGeeksBlog Premium member and access our content ad-free with additional perks.
- Click the Apple menu and open System Settings.
- Click Wi-Fi and then choose Details next to the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to.
- From the left side, select DNS.
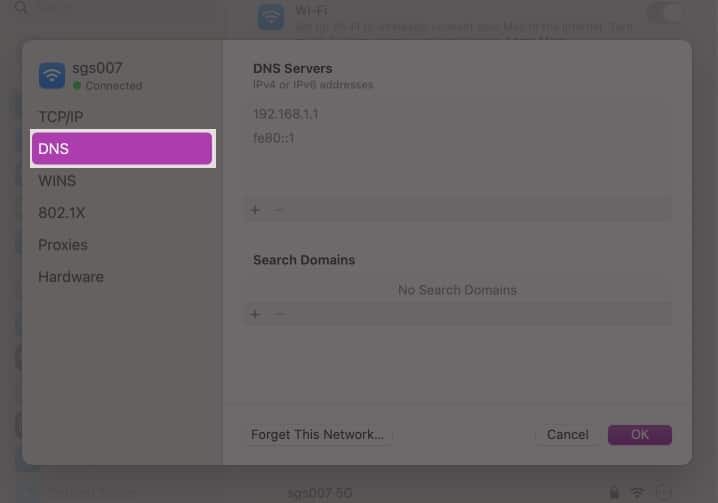
- Click the ‘+’ symbol under DNS Servers.
- Type in the following IP address: 8.8.8.8
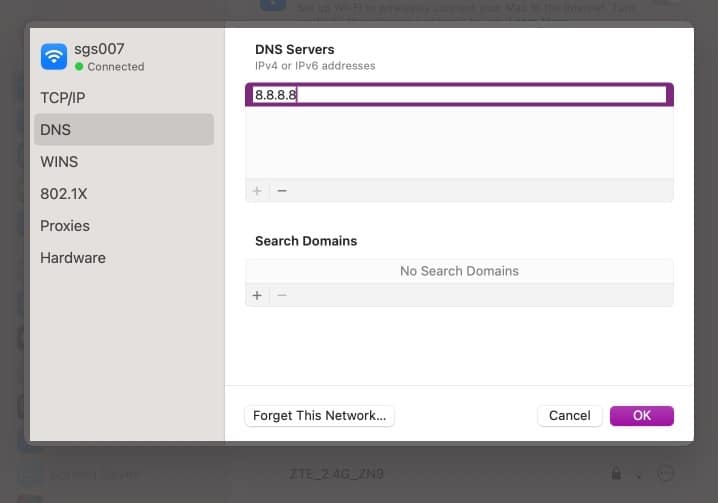
- Press the Return key on your keyboard.
- Click ‘+’ again to add a secondary DNS server.
- Type in 8.8.4.4 and press Return.
- Close System Settings and check if Wi-Fi works for you now.
6. Turn off Firewall
In rare cases, the firewall feature on your macOS or some third-party firewall software might disrupt your Wi-Fi connection. Follow the steps below to turn off the built-in firewall in macOS Sequoia.
- Click on the Apple menu and open System Settings.
- Click on Network and select Firewall.
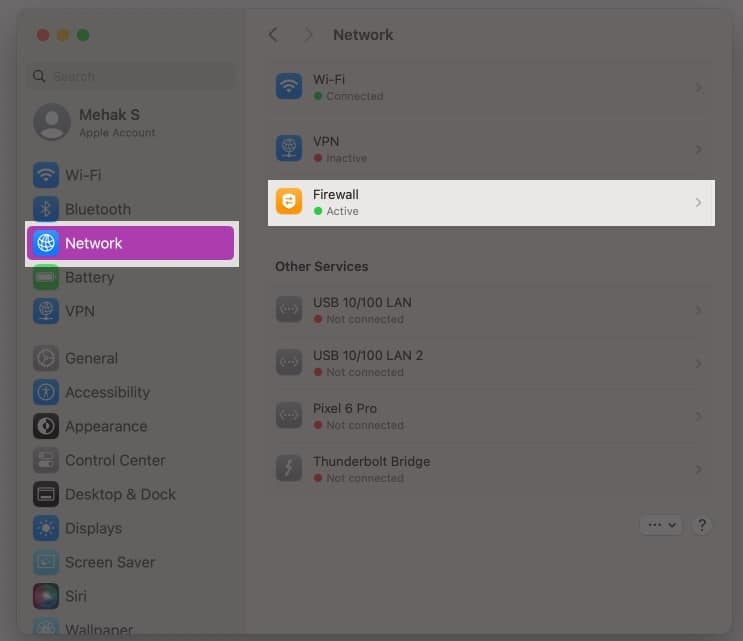
- Toggle off the Firewall and then close System Settings.
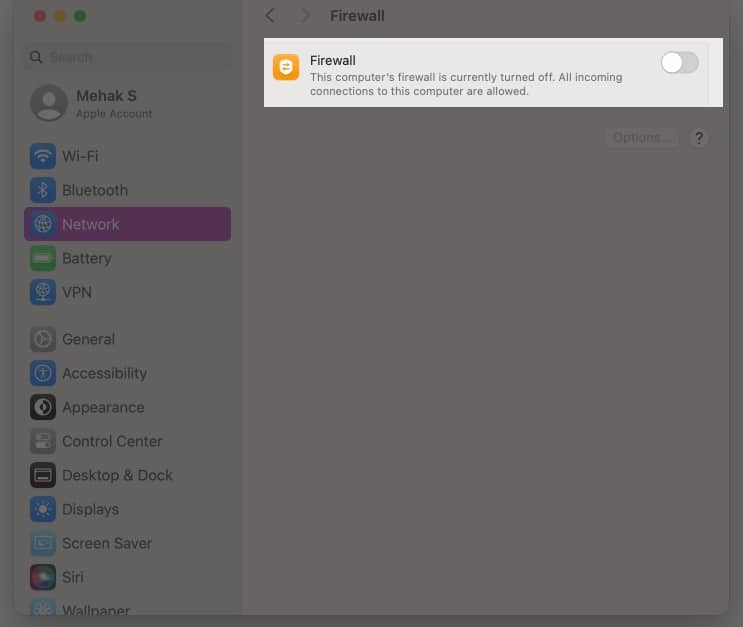
Now, check if your Wi-Fi works. Similarly, if you use a third-party firewall, disable it and check your Wi-Fi connection.
7. Check third-party apps
Many third-party apps like VPNs, parental control, or antivirus software can cause Wi-Fi issues on your Mac especially after you update your macOS.
Therefore, if none of the steps given above have fixed your Wi-Fi issues, try to disable or uninstall any third-party apps that could be causing the problem.
8. Run Wireless Diagnostics
If you continue to face Wi-Fi issues on your Mac, you can run wireless diagnostics to help identify the problem. Here’s how:
- Close all open apps.
- Try to connect to the Wi-Fi network if you aren’t already connected.
- Press and hold the Option key on the keyboard and click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar. Click on Open Wireless Diagnostics.
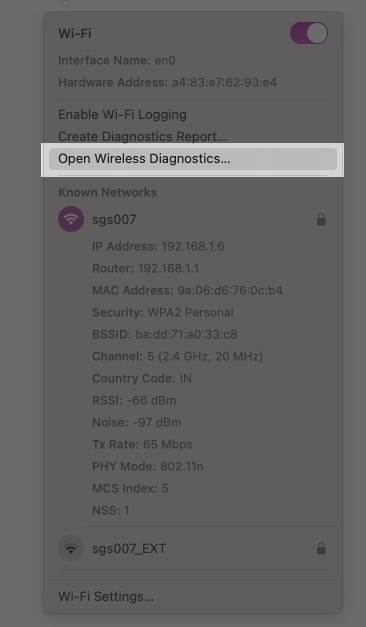
- Follow the onscreen instructions to analyze your network connection.
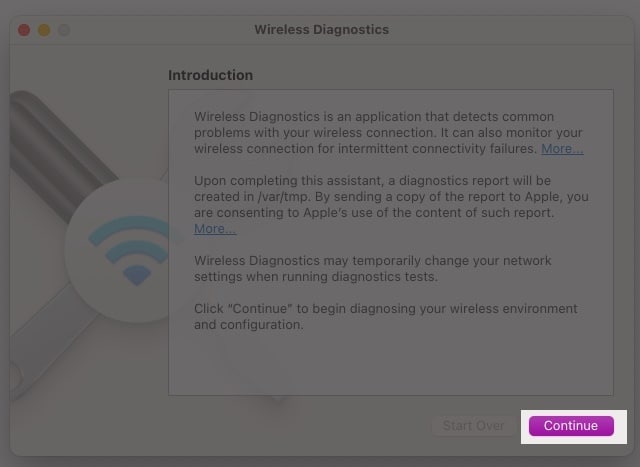
- Your Mac will analyze any Wi-Fi issues, and you can click the Info buttons in the Summary pane to learn more about each item listed.
Signing off
Hopefully, I have helped you fix Wi-Fi issues on your Mac. If you continue to face problems, contacting Apple Support for assistance is a good idea.
FAQs
Wi-Fi problems may be caused by many reasons, such as a software glitch or errors in your network settings. Start by restarting your router and your Mac to check if this fixes the issue. If not, you can reconfigure the Wi-Fi network, change DNS servers, disable the firewall, or run wireless diagnostics on your Mac.
When the Mac and Wi-Fi router are placed at a distance, signal strength is low. As a result, your Mac may often drop the connection. Similarly, such issues may occur if you have not restarted your router or your Mac in a long time. Move closer to your router and restart both your router and your Mac to help fix the issue.
Quit all open apps first. Then, try connecting to a Wi-Fi network, if you aren’t already connected. Next, press the option key and click on the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu bar. Finally, click on ‘Open Wireless Diagnostics’ and follow the on-screen instructions.
You might want to read these posts as well:

